Most horse owners say they take better care of their equine partners than themselves. While many maintenance treatments and products could be considered a luxury, veterinary chiropractic adjustments do not fall into that category. Palm Beach Equine Clinic’s Dr. Ryan Lukens is a certified Veterinary Medical Manipulation Practitioner from the Chi Institute in Ocala, FL, and recommends all horses can benefit from regular chiropractic adjustments.
From minis to draft horses and pasture pets to top sport mounts, the parasympathetic stimulation triggered by chiropractic adjustments improves multiple facets of health for any equine. Therefore, veterinary chiropractic adjustments improve more than just athletic performance, and for sport horses, Dr. Lukens considers them a necessity.
According to Dr. Lukens, the benefits of veterinary chiropractic adjustments include:
- Relief of pain and soreness
- Increase in range of motion
- Reversal of muscle atrophy through increased frequency of nerve activation
- Increase in speed and accuracy of athletic movement
- Adjustments can help calm the “fight or flight” response
Dr. Lukens outlines the “must know” details for any sport horse owner:
-
Major Adjustment Points
There are 205 bones that comprise the skeleton of a horse, however, the equine chiropractor does not just adjust the skeleton. It is important to improve motion at segmented levels that involve bones and the supporting soft tissue structures and nerves. “Motion palpation” is used to test moving segments. If a segment is not moving freely in the appropriate directional planes, the equine chiropractor can perform an adjustment to correct the restriction of this movement.
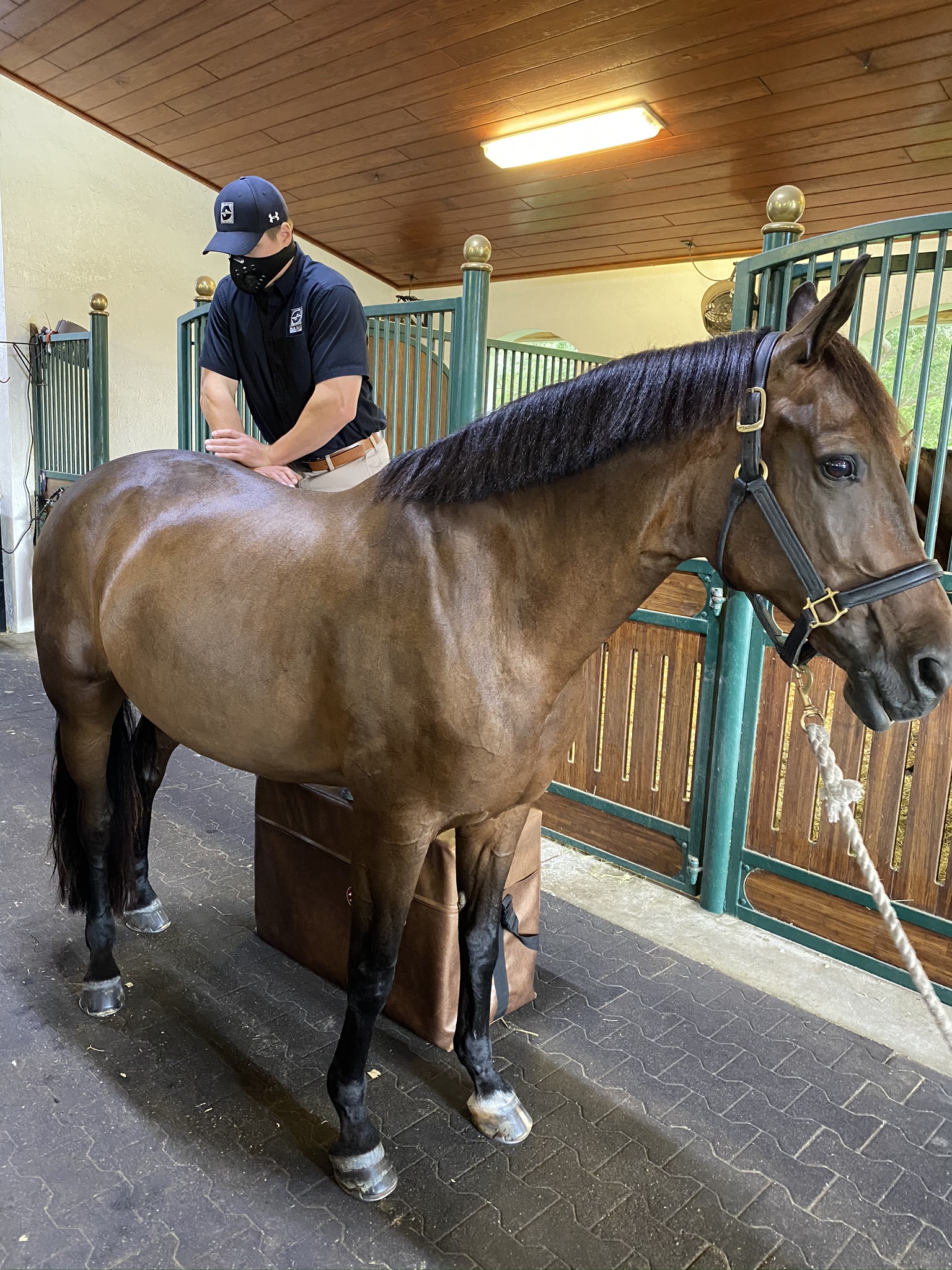

Photo courtesy of Palm Beach Equine Clinic
Major adjustment points include the:
- Mandible and tongue
- Temporomandibular joint (TMJ)
- Poll and cervical vertebrae
- Withers and sternum
- Front and hind limbs
- Thoracic and lumbar vertebrae
- Pelvis/sacrum
-
Every Horse Is Different
Veterinary chiropractic adjustments can be different for each horse and are often based on their discipline. The most common adjustments for various performance horses include:
Dressage: Balance is essential for dressage. The major points of balance affected by veterinary chiropractic work are the TMJ, hyoid, sternum, and cervical facets. Other common adjustments affected by lateral work include the shoulders, elbows, and pelvis.
Hunter/Jumper: Hunters and jumpers typically benefit from vertebral adjustments of the lumbar and upper cervical regions, ribs, sternum, front distal limbs, and the shoulders.
Eventing: Most eventing horses benefit from adjustments to the pelvis, all cervical vertebrae, TMJ, ribs, and the shoulders.
Western Disciplines: Reiners benefit from adjustments to their right shoulder, lower cervical facets, withers, and pelvis. Barrel racers benefit from shoulder, sacroiliac, and hip joint adjustments.
-
Tips for Before and After an Adjustment
It is important that dental and farrier work is not overdue before veterinary chiropractic adjustments. Sharp dental points can cause adjustments to hold for shorter periods of time, especially in the poll, TMJ, and cervical vertebrae. In addition, if a horse is currently not shod well or has recently pulled a shoe, the adjustments of their limbs, back, pelvis, and sacrum may not provide long-lasting benefits.
Horses can be ridden and have a normal day before an appointment. They should not be ridden for the remainder of the day after an adjustment, but they can be turned out to pasture. Horses can be ridden as normal the following day, and it is a good idea to follow up with the veterinarian about how they felt.
-
Solving Common Issues
Several common issues are often solved by a veterinary chiropractic adjustment. For jumpers, changes in jumping style (i.e. landing away from a front limb, only jumping off of a certain lead) and performance (hitting more rails than normal) could indicate a lack of range of motion that can often be corrected through a proper adjustment or series of adjustments.
For dressage horses, a change in balance could result in head tilting, not working through the back, lifting the lower cervical curve, or the hind limbs not following the path of the front limbs. That balance can often be reestablished with an adjustment.
In the western disciplines, a decrease in acceleration and turning can be indicative of the need for adjustments.
-
Choosing Your Equine Chiropractor
A veterinarian trained in chiropractic adjustments is the safest choice for the horse. A veterinarian’s extensive knowledge of anatomy and understanding of when not to adjust a horse is an important part of ensuring the horse’s safety and well-being. If done improperly, adjustments can have adverse effects.
For a more in-depth explanation of equine chiropractic adjustments, click HERE to read the full article from Palm Beach Equine Clinic.
NOTE: These guidelines are only suggestions, and you should always follow the specific instructions from your veterinarian.
Have questions about utilizing BarnManager or want to give it a try for yourself? Request a live demo here!
BarnManager is designed to be a part of your team, with the compatibility and credentials necessary to improve communication, simplify the management of horses, and get you out of the office, off the phone calls, and into the barn with the horses you care about! Click here to get a free demo and find out more!